New Tungsten Carbide Grades Now Available
We’ve expanded our portfolio with additional General Carbide grades to help you fine-tune performance for your most demanding applications. Explore the updated Grade Specification Charts to compare hardness, density, grain size, and strength values at a glance.
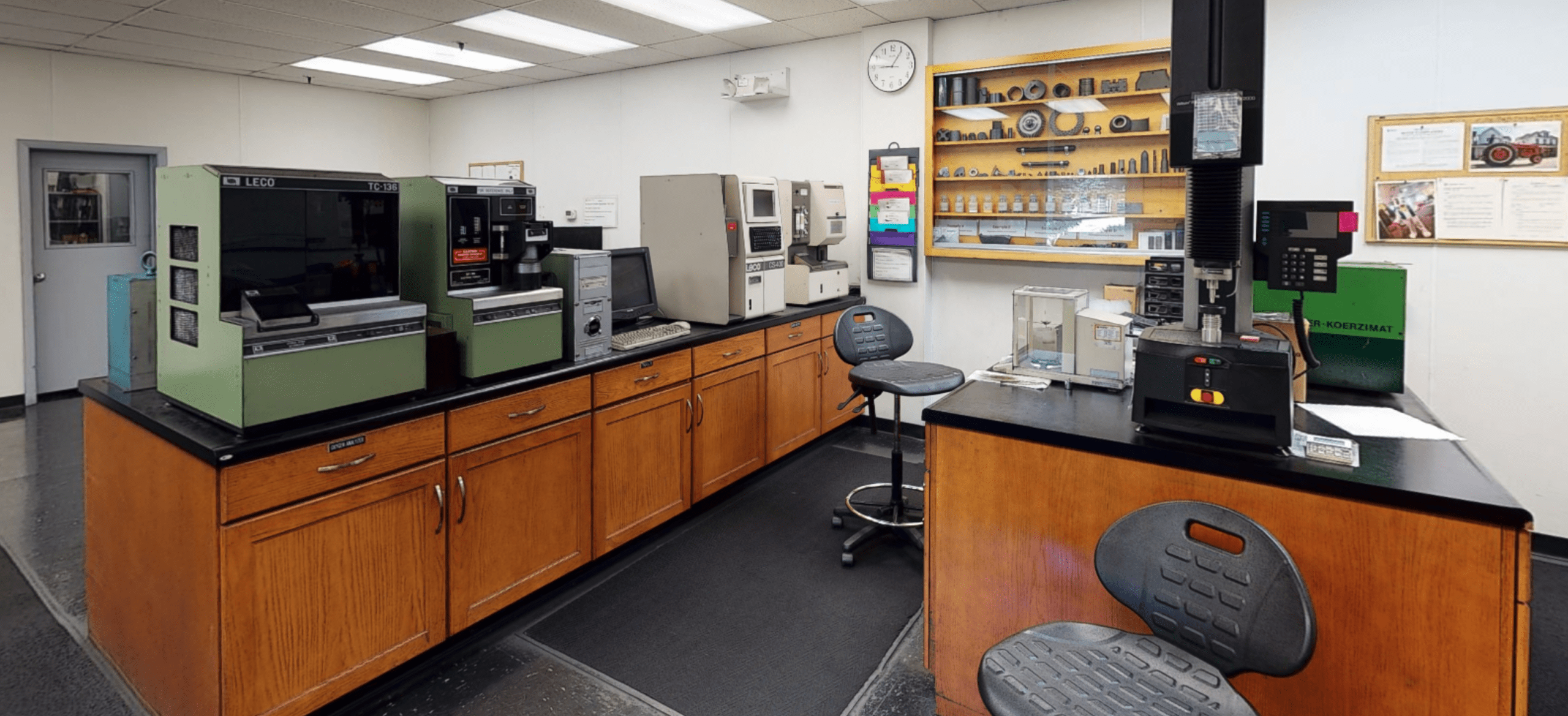
Making the Grades
Tungsten carbide (WC), also referred to as cemented carbide, is a composite material manufactured by a process called powder metallurgy. Tungsten carbide powder, generally ranging in proportion between 70%-97% of the total weight, is mixed with a binder metal, usually cobalt or nickel, compacted in a die and then sintered in a furnace.
The term “cemented” refers to the tungsten carbide particles being captured in the metallic binder material and “cemented” together, forming a metallurgical bond between the tungsten carbide particles and the binder (WC – Co), in the sintering process. The cemented carbide industry commonly refers to this
material as simply “carbide”, although the terms tungsten carbide and cemented carbide are used interchangeably.





